Clinical
Case Discussion
Case
Presentation: A Man with
Two
Synchronous
and
Symptomatic Malignancies
Related
to
Smoking
Alberto
Briganti
a , * ,Gianluca
Giannarini
ba
Division
of
Oncology/Urology
Unit,
Urological
Research
Institute,
IRCCS
Ospedale
San
Raffaele,
Milan,
Italy;
b
Urology
Unit,
Academic
Medical
Centre
Hospital
Santa Maria
della Misericordia, Udine,
Italy
A
77-yr-old man
presented
in
the
emergency
room
with
abdominal
pain,
fatigue,
jaundice,
and
gross
haematuria.
The
patient
had
no
significant
comorbidities
and
had
been
in
good
general
condition.
The
patient
was
on
alfuzosin
and
dutasteride
for
symptomatic
benign
prostatic
hyper-
plasia.
He
had moderate
alcohol
consumption
and was
a
heavy
smoker
(approximately
40
cigarettes
per
day
since
age
20
yr).
The man
became
symptomatic
roughly
2 mo
prior
to
hospital
admission. Over
this
time,
he
lost
approximately
5 kg
in
weight,
and
his
abdominal
pain
became
more
severe.
He
rated
it
5
on
a
scale
from
0
to
10,
with
10
indicating
the most
severe
pain.
The
pain was
chronic
with exacerbation and was
located
in
the mesogastric area.
Approximately 5 d before hospital admission, he developed
jaundice
associated
with
increasing
pain
and
persistent
gross
haematuria.
On
admission
to
the
hospital,
he
received
blood
examinations,
abdominopelvic
ultrasound,
and
urine
anal-
ysis. Complete blood count and
renal
function were normal,
as
were
blood
levels
of
electrolytes,
glucose,
calcium,
phosphorus,
magnesium,
total
protein,
and
albumin;
however,
increasing
values
of
total
bilirubin,
conjugated
bilirubin,
aspartate
aminotransferase,
alanine
aminotrans-
ferase, alkaline phosphatase, and
g
-glutamyl transpeptidase
were
found.
The
ultrasound
showed
dilation
of
the
biliary
ducts
and
bilateral
4-
to
6-cm
Bosniak
I
cysts.
At
urine
analysis,
high
erythrocyte
levels were
found.
Abdominal
and
thoracic
contrast-enhanced
computed
tomography
scans
were
performed
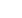
( Fig. 1).
Intrahepatic
biliary
distension
was
evident,
and
the
common
biliary
ducts
in
prepancreatic
and
intrapancreatic
areas
appeared
thickened.
Hydropic
gallbladder
was
also
noted.
A
small
nodule
(
<
1
cm)
in
the
inferior
left
pulmonary
lobe
was
found.
Moreover,
in
addition
to
bilateral
Bosniak
I
renal
cysts,
an
endophytic
contrast-enhanced mass highly
suspi-
cious
for upper urinary
tract carcinoma
infiltrating
the renal
pelvis
was
found
in
the
left
kidney
(maximum
diameter
4
cm). No
retroperitoneal
lymphadenopathies were
noted.
Endoscopic
ultrasound
was
performed,
and
intrahepatic
biliary
and
common
bile
duct
distension was
found with
a
complete
occlusion
of
the
hepatic
hilum.
Hypoechoic
lesions were
reported
on
the
gallbladder,
duodenum,
and
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y F O C U S 1 ( 2 0 1 5 ) 9 0 – 9 3available
at
www.sciencedirect.comjournal
homepage:
www.europeanurology.comFig.
1
–
Cross-section
computed
tomography
image
showing
a
filling
defect
in
the
left
renal
pelvis,
in
keeping with
urothelial
cell
carcinoma
(white
arrowhead),
and
a mass
around
the
common
bile
duct
(with
internal
drainage)
is
seen
(white
arrow).
* Corresponding
author. Division
of Oncology/Urology Unit, Urological
Research
Institute,
IRCCS Ospedale
San
Raffaele, Milan,
Italy.
address:
briganti.alberto@hsr.it(A.
Briganti).
2405-4569/
#
2015
European
Association
of Urology.
Published
by
Elsevier
B.V.
All
rights
reserved.