disorders, chronic
inflammatory or autoimmune diseases, or prior steroid
therapy, the remaining 394 patients were assessed
in further analyses. The
median
follow-up
of
the
entire
cohort was
30 mo
(interquartile
range
[IQR]:
15–63 mo).
RNU
was
performed
according
to
the
standard
criteria,
that
is,
extrafascial dissection of
the kidney with
the
entire
length of
the ureter
and
an
adjacent
segment
of
the
bladder
cuff.
Surgical
specimens were
evaluated
at
each
institution.
All
specimens
were
histologically
confirmed
to
be
UC.
No
patient
underwent
endoscopic
resection
prior
to
RNU.
Dissection
of
regional
lymph
nodes
was
performed
in
patients with
nodes
that were
found
to
be
enlarged
in
a
preoperative
evaluation
or
in
those who were
suspected
of having
enlarged nodes
at
intraoperative
inspection.
Indeed,
37
patients
underwent
lymph
node
dissection
at
the
time
of
RNU.
Adjuvant
chemotherapy
following
RNU
was
administered
to
88
patients.
Tumors were staged according
to
the 2002 American
Joint Committee
on Cancer
and Union
for
International Cancer Control TNM
classification
and
graded
according
to
the
1973 World Health Organization
classifica-
tion. Lymphovascular
invasion
(LVI) was defined as
the presence of
tumor
cells within
an
endothelium-lined
space without
underlying muscular
walls. The presence of concomitant carcinoma
in situ (CIS) was assessed
in
every
representative
section. Tumor
location was divided
into
two areas,
the renal pelvis or the ureter, based on the
location of the dominant
lesion.
The
assessment
of
preoperative
blood
data
was
performed
just
before any of
the manipulations,
such as
retrograde pyelography
and/or
ureteroscopic evaluation with tumor biopsy, whereas RNUwas generally
performed within 1 mo
following manipulation. NLR was defined as
the
absolute neutrophil count divided by
the absolute
lymphocyte count, and
patients with NLR
>
3.0 were defined as having elevated NLR
[8,9]. Blood
data
concerning plasma fibrinogen
levels were determined by
the Clauss
method,
and
plasma
fibrinogen
levels
390 mg/dl
were
defined
as
elevated
[11,17].
In
this study, patients with serum CRP
levels
>
0.5 mg/dl
were
defined
as having
elevated
CRP
[12].
The
cumulative marker
score
(CMS)
was
defined
as
the
number
of
elevated
preoperative
levels
of
NLR,
plasma
fibrinogen,
and
serum
CRP
and
divided
into
four
groups
(0,
1, 2,
and 3).
Patients were
generally
followed
every
3–4 mo
for
2
yr
following
RNU,
every
6 mo
for
the
next
3
yr,
and
then
every
6–12 mo
thereafter.
Follow-up
consisted
of
history,
physical
examination,
routine
blood
work, urinary cytology, chest
radiography, and cystoscopic evaluation of
the urinary bladder. Radiographic evaluations of
computed
tomography
(CT),
magnetic
resonance
imaging,
and/or
excretory
urograms
were
performed
every 6 mo
for
the first 5 yr
and
annually
thereafter. Elective
bone
scans
and
chest
CT were
performed when
clinically
indicated.
Disease
recurrence was
defined
as
any
documented
first
relapse
by
radiography-
or
pathology-proven
failure
in nonbladder
lesions,
such
as
the
operative
site,
regional
lymph
nodes,
or
distant
metastasis.
The
occurrence of urothelial
carcinoma
in
the bladder
or
contralateral upper
tract
was
not
coded
as
disease
recurrence.
The
cause
of
death
was
determined by the attending physicians, by chart reviews corroborated by
death
certificates,
or
by
death
certificates
alone
at
each
institution.
To
reduce bias
in attribution of
the cause of death, only patients who had UC
listed on the deathcertificatewere considered tohave died ofUTUC forthis
study
[18]. All
patients who were
coded
as
dead
of
cancer had
previous
disease
recurrence.
2.1.
Statistical
analysis
The
variables
of different
groups were
compared using
the
chi-square
test
or
the
Mann-Whitney
U
test,
as
appropriate.
Spearman
rank
correlation
coefficient
was
used
to
compare
continuous
variables.
Survival
curves were
estimated
using
the Kaplan-Meier method, with
the
log-rank
test used
to assess
significance. Univariate and multivari-
ate
Cox
regression
models
were
used
to
evaluate
time
to
disease
recurrence
and
cancer-specific
and
all-cause mortality. The predictive
accuracy
of
the multivariate models was
estimated
by
the
area
under
the
receiver
operating
characteristic
curve.
Changes
in
predictive
accuracy were
quantified with
the Harrell
concordance
index
[19,20] ,and
area
under
the
curve
internal
validation
was
performed
using
200 bootstrap
resamples.
Predictive
accuracy
estimates
are
expressed
as
percentages
and were
compared
using
the Mantel-Haenszel
test.
Differences
among
groups
were
regarded
as
significant
when
p
<
0.05.
Statistical
analyses
were
performed
with
the
R
Statistical
Language version 2.9
(R Foundation, Vienna, Austria)
and SPSS version
22.0
(IBM
Corp., Armonk, NY, USA)
statistical
software
package.
3.
Results
The median
age of
the
entire
cohort was 70
yr
(IQR: 63–77
yr). Men accounted
for 73.4%
(289 patients) and women
for
26.6%
(105
patients).
The median
values
of
preoperative
NLR,
plasma
fibrinogen,
and
CRP were
2.4,
364 mg/dl,
and
0.25 mg/dl,
respectively.
Table 1presents
the
clinicopatho-
logic parameters of
the 394 patients. Patients with elevated
NLR
tended
to
be
older
and
had
a
higher
incidence
of
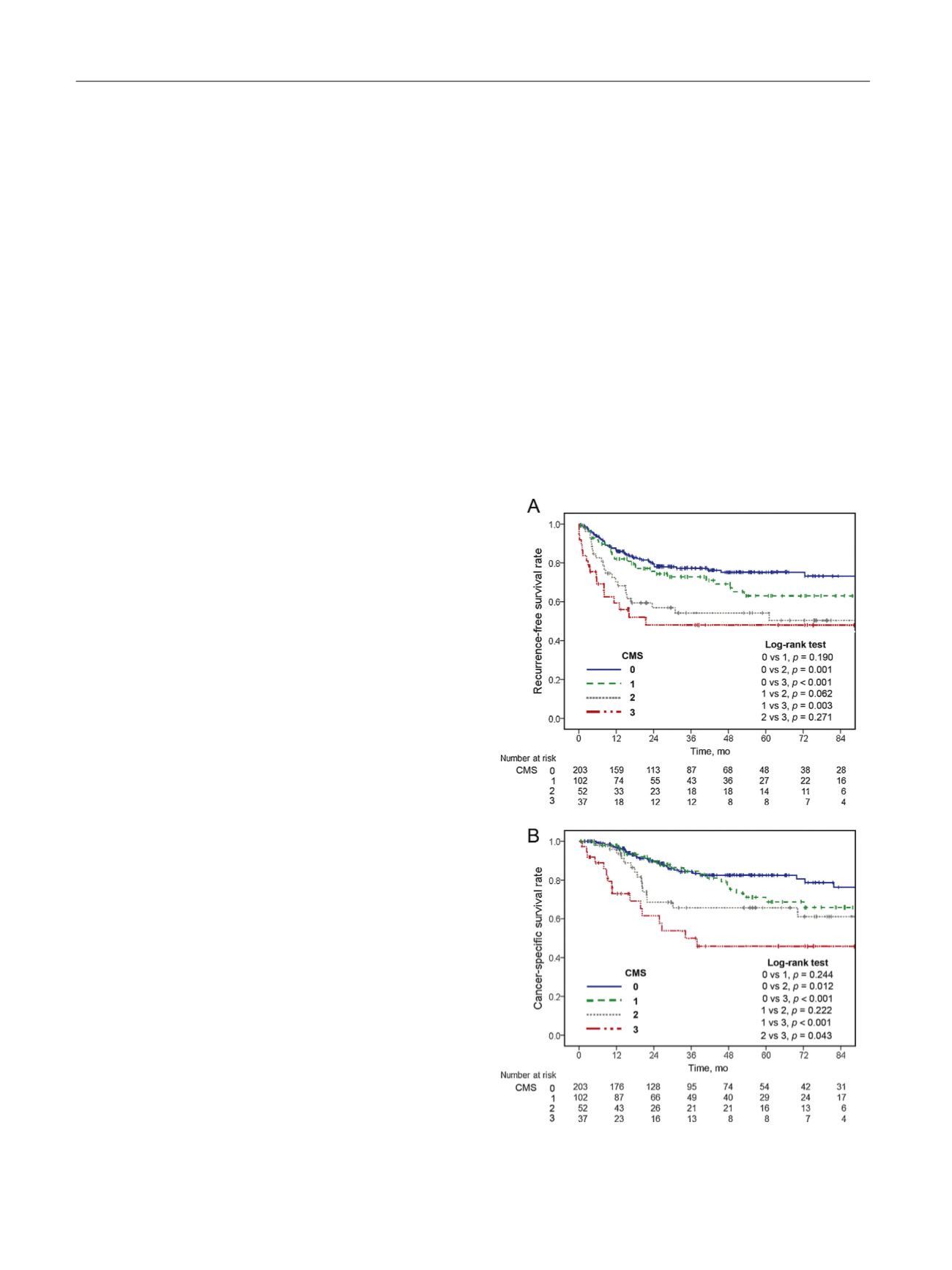
Fig.
1
–
(A)
Recurrence-free
and
(B)
cancer-specific
survival
rates
in
394
patients who
underwent
radical
nephroureterectomy
according
to
the
cumulative marker
score.
CMS = cumulative marker
score.
E U R O P E A N
U R O L O G Y
F O C U S
1
( 2 0 1 5
)
5 4 – 6 3
56